The FlowVR plugin lets you write FlowVR modules without knowing any specific FlowVR API calls. Properly created PDI configuration file allows you to care only about proper input/output calls, but this plugin does not support the full FlowVR feature set.
The root of FlowVR plugin configuration (named flowvr), is a dictionary that contains the following keys:
For now, only available component is module and this is a default value, but this can be expanded to filter and synchronizer in the future. Configuration example:
The plugin will call wait funciton every time given descriptors will be shared with PDI_IN access direction. This descriptor must be an integer type and the status returned from this call will be written as a response. Configuration example:
Defines on which events the plugin calls the wait function. The value can be either single event name or the array of events names (both examples presented below). This method of calling wait should be avoided if possible, because it's not returning the wait status. Configuration examples:
PDI will copy the status of the module to the given descriptor. The same as the wait_on it can be a single name or an array of names. Configuration example:
Defines on which events the plugin calls the abort function which will stop the flowvr application. The value can be either single event name or the array of events names. Configuration examples:
Defining this subtree tells PDI that the plugin should be initialized not on PDI_init, but on given event.
This node can be for reading rank and size of the world, but also can be for setting this values. get_rank will copy process's rank to given descriptor on share, get_size will save the world size the same way. Example:
Values (use $ expression) from descriptors defined in set_rank and set_size will be passed to flowvr and set the environment. Setting this parameters must occur before plugin initialization. For this you need to use init_on event and call this event after setting rank and size.
Single program can run several modules at once. To make it work just create array of modules in flowvr tree. Configuration example:
Input ports are defined in input_ports tree. Each port is defined by name and Message it will receive. You can add event_port: true to define this as event port (non-blocking).
Output ports are defined in output_ports tree. Each port is defined by name and Message it will send.
Flowvr message consists of payload and stamps. The payload is defined by user by a specific key in port definition:
| key | message type |
|---|---|
| "data" | Data payload |
| "chunks" | Chunk payload |
| "event_button" | Event button payload |
| "event_mouse" | Event mouse payload |
If none of the message type will be given, plugin will create a STAMP port (message has no payload). stamps are described in Stamp section.
Requires data key in a port tree. This configuration means that module will send simple buffer. The plugin doesn't know the type of sending data. The value of data key is the name of the descriptor where:
Example of data in output port:
The user can not always predict how many data will receive. In this case size node type must be a name of metadata where to write the size of received payload. This metadata will hold the size of received array. The size property of descriptor should be divided by size of single element. Example of receiving unknown payload size:
In case that you want to send only a part of the data from descriptor you can specify it in copy_data_selection tree defining datatype the same way as for descriptors. Simple example:
Requires chunks key in a port tree. This configuration means that module will send several buffers in one payload. Value of the chunks key is the list of Data payload.
WARNING
After each wait, the first access to the any descriptor (that belongs to the chunks) will allocate the memory for the all descriptors. This means that all sizes (if stored as metadata) should be set before first access to any of the descriptors.
Requires event_button key in a port tree. The payload holds the values of the keyboard keys pressed during iteration.
The full list of predefined keys:
| key in configuration | key on keyboard |
|---|---|
| KEY_F1 | F1 |
| KEY_F2 | F2 |
| KEY_F3 | F3 |
| KEY_F4 | F4 |
| KEY_F5 | F5 |
| KEY_F6 | F6 |
| KEY_F7 | F7 |
| KEY_F8 | F8 |
| KEY_F9 | F9 |
| KEY_F10 | F10 |
| KEY_F11 | F11 |
| KEY_F12 | F12 |
| KEY_UP | Up Arrow |
| KEY_DOWN | Down Arrow |
| KEY_LEFT | Left Arrow |
| KEY_RIGHT | Right Arrow |
| KEY_PAGE_UP | Page Up |
| KEY_PAGE_DOWN | Page Down |
| KEY_HOME | Home |
| KEY_END | End |
| KEY_INSERT | Insert |
Value for each key in configuration is a descriptor of integer type. You need to make sure that you are setting this descriptors with correct values on each iteration. Example of configuration with arrow buttons:
Requires event_mouse key in a port tree. The payload holds the values of the mouse keys pressed and cursor position during iteration. The button state is saved in descriptors of integer type and a cursor position in an array of 2 floats.
Available keys in event_mouse tree:
| key | description |
|---|---|
| POS_XY | cursor position |
| LEFT_BUTTON | left mouse button |
| MIDDLE_BUTTON | middle mouse button |
| RIGHT_BUTTON | right mouse button |
Example of configuration with all keys defined:
The stamps key must be defined in a port tree. The value of stamps is simply a map with the stamp name and descriptor name. The given descriptor must have a valid PDI type, limited to:
intfloatarray of intsarray of floatsarray of charsExample of message with Data payload and 2 stamps:
For output port stamp can be also define as an expression, but stamp will need type definition in this case. Example of expression stamp:
For now only int and string stamps are supported as expression.
FlowVR plugin uses 2 ways to handle data reading and writing:
Stamps are always copied from descriptor to flowvr message.
Path to the examples:
Original flowvr source files are in directories flowvr_original.
cd pdi_plugin-flowvr/src/FLOWVR_PLUGIN-build/examplessource flowvr-config.sh. Now your environment is ready.flowvrd --top$example_name directory generate the flowvr configuration files by: python $example_name.py and run example by: flowvr $example_nameConsists of 2 modules:
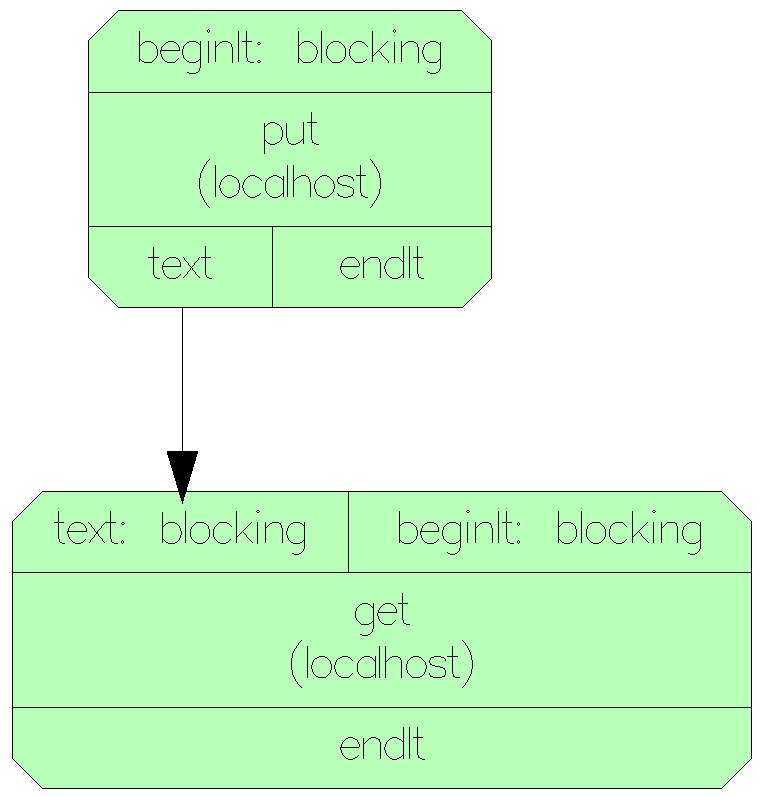
putput.cxxput.ymloutput port named texttype: {type: array, subtype: char, size: 4} #"tic" or "tac"type: inttype: {type: array, subtype: int, size: 2}getget.cxxget.ymlinput port named textput modulestamp:type: {type: array, subtype: char, size: 256}Network of the application:
Consists of 3 modules:
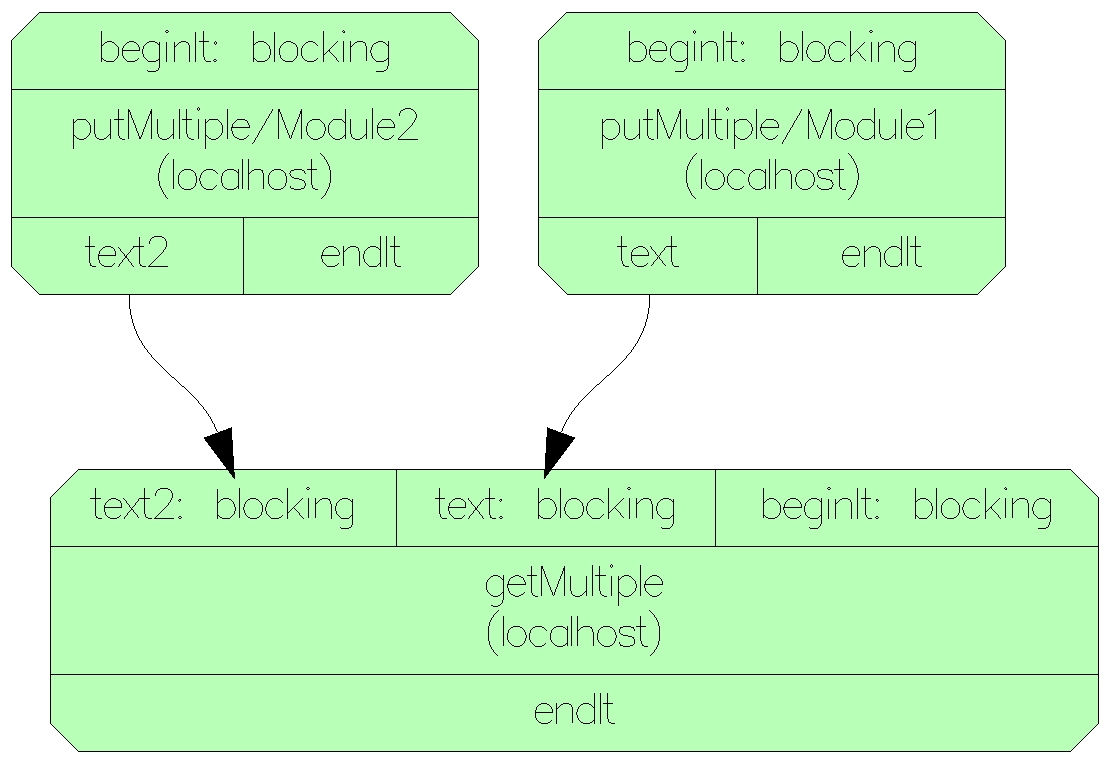
putMulitpleputMulitple.cxxputMulitple.ymloutput port named text, second text2type: {type: array, subtype: char, size: 4} # first "tic" or "tac", second "TIC" or "TAC"it (predefined flowvr stamp): type: intgetMulitplegetMulitple.cxxgetMulitple.ymlinput ports named text and text2putMulitple modulesstamp:type: {type: array, subtype: char, size: 256}Network of the application:
Consists of 3 modules:
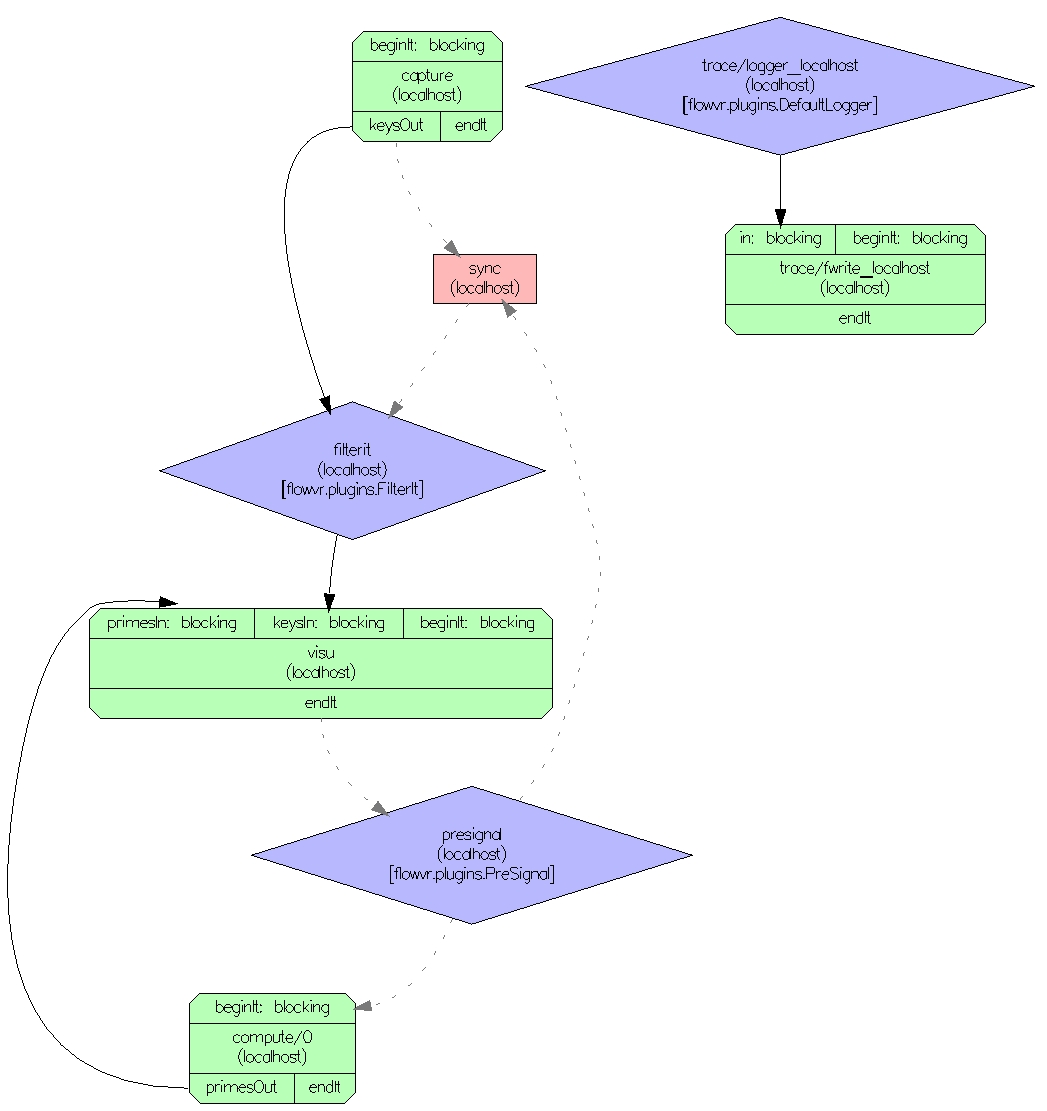
capturecapture.cxxcapture.ymloutput port named keysOutevent_button (payload):computecompute.cxxcompute.ymloutput port named primesOuttype: {type: array, subtype: int, size: $tempPrimeNumbersMaxCount}type: intvisuvisu.cxxvisu.ymlinput ports named primesIn and keysIncapture and compute modulesNetwork of the application:
Consists of 2 modules:
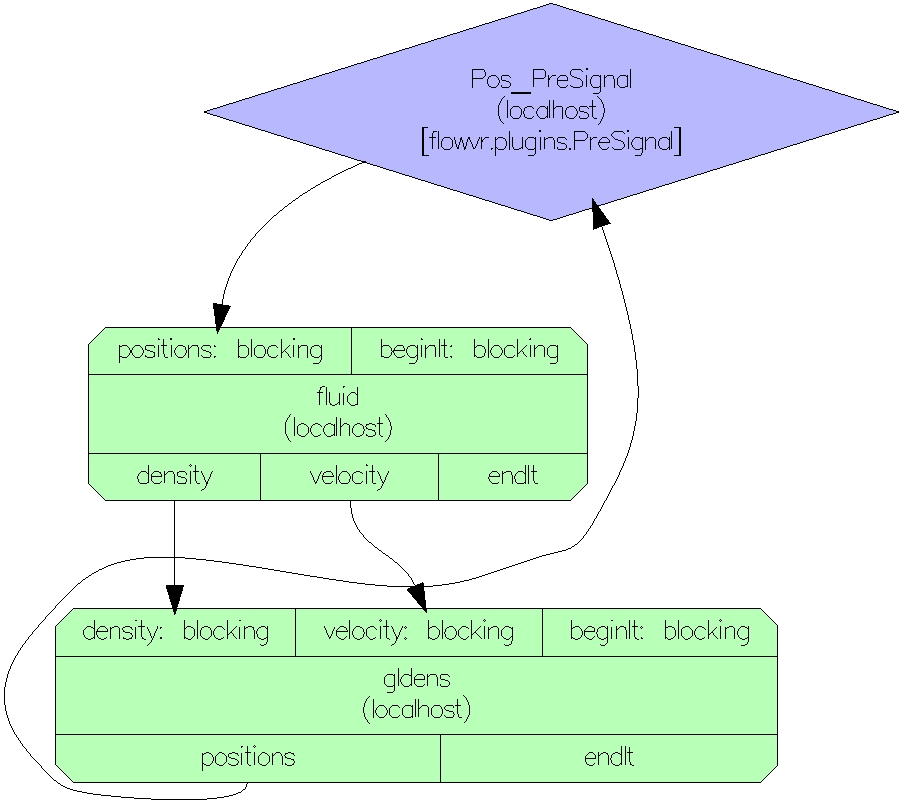
fluidfluid.cxxfluid.ymlinput port named positiongldens moduleoutput ports named velocity and densityvelocity and density both sends message with:type: {type: array, subtype: char, size: [$NX * 2, $NY]} # where NX and NY is metadatatype: {type: array, subtype: int, size: 2}type: {type: array, subtype: int, size: 2}gldensgldens.cxxgldens.ymlinput ports named velocity and densityfluid moduleoutput port named positiontype: {type: array, subtype: float, size: 3}velocity and density ports:type: {type: array, subtype: char, size: $velocitySize} # velocitySize is defined as metadata Here velocitySize must be preceded with $ to let plugin to write the size there. The velocitySize descriptor will store a valid size after accessing the velocity descriptor, because only then plugin will write size.Network of the application: